
The Grammarsaurus Science Curriculum aligns with the English National Curriculum. The scientific knowledge and conceptual understanding has been mapped to ensure that pupils following our sequence of learning have ample opportunity to make progress in science by knowing and remembering more science content.
Curriculum Aims
- Develop scientific knowledge and conceptual understanding through the specific disciplines of biology, chemistry and physics.
- Develop understanding of the nature, processes and methods of science through different types of science enquiries that help pupils to answer scientific questions about the world around them.
- To equip pupils with the scientific knowledge required to understand the uses and implications of science, today and for the future.
Y1
Animals, including
humans (Part 1)

How can we group animals?
During this unit of work, children will learn about different common animals and be able to discuss their features using scientific language such as feathers, beak, scales, fins etc. They will begin to identify similarities and differences between different animals. Children will also look at the diets of different animals and compare these.
What makes us human?
In this unit, children will focus on humans, identifying body parts and linking these to senses as well as discussing the similarities and differences between humans.
Everyday materials
Why do we use different materials for different things?
During this unit of work, children will learn about different materials and be able to identify objects made from different materials. They will be able to identify the difference between an object and the material from which it is made. Throughout the unit, they will be helping Blot, an alien from the Planet Glog, who does not know anything about materials. Children will group and sort different materials based on their properties. They will also have the opportunity to investigate different materials to see which material would be best to make an umbrella and curtains.
Seasonal changes

How does the weather change during the different seasons?
During this unit of work, children will learn about the four different seasons. This topic is best done throughout the year in the appropriate season so children can observe the season first hand. The first four lessons cover the four seasons and can be completed in any order.
Plants

How can we identify different plants and trees?
During this unit of work, children will learn about different wild and common plants and label their basic features. They will look for wild plants in their local area and discuss plants that we can eat. Children will then look at trees and their basic features. They will look at the difference between deciduous and evergreen trees before looking at different leaves from trees. Children will plant a seed in lesson 3 and keep a plant diary during the rest of the lessons to show how their plant grows and changes.
Y2
Animals, including
humans
Why do we need to keep healthy?
During this unit of work, children will learn about the basic needs that all humans need to survive and live. They will study more closely the importance of exercise, a healthy diet and good hygiene as ways to keep us healthy. They will also look at offspring of different animals and how they develop and change into adults as they grow. Finally, children will also look at ways to keep themselves from becoming ill as well as things they can do if they do become ill.
Everyday materials

How are materials chosen in design?
During this unit of work, children will learn about different everyday materials such as wood, metal, plastic, glass, rubber, rock, fabric, paper and brick. They will identify the properties of these materials and conduct investigations to explore how different materials are better suited for different objects through well-known stories. Children will also explore how some of these materials can be changed by squashing, bending, twisting and stretching them.
Living things and
their habitats

How do we know something is alive?
During this unit of work, children will learn about living things and their habitats. They will start the unit of work looking at whether things are living, dead or have never been alive. They will then look at microhabitats and larger habitats identifying some animals that may live there. Children will then conduct an investigation to see which type of conditions woodlice prefer in their habitat. After that they will look at how living things are adapted to their environment. Finally, they will look at food chains within habitats.
Plants

How do seeds and bulbs grow into healthy plants?
During this unit of work, children will learn about different seeds and bulbs. They will learn about plants we can eat and begin to gather seeds. They will also look at what plants need to grow and what they need to continue to grow and stay healthy.
Y3
Animals, including
humans
How do the systems inside our body work to make a healthy human?
During this unit of work, children will learn about the structure of the human skeleton and how the muscles also work alongside the skeleton to support and protect the human body. They will then look at how skeletons differ in different animals. Finally, children will look at nutrition and the importance of eating a healthy diet.
Rocks

How can we classify rocks?
During this unit of work, children will explore different rocks and soils. They will classify and group together rocks based on their appearance as well as their physical properties. They will learn how the Earth is made up of different rocks and fossils and begin to explain how some of the different rocks are formed. Children will also look at fossils, what they are and how they are formed in rock.
Magnets
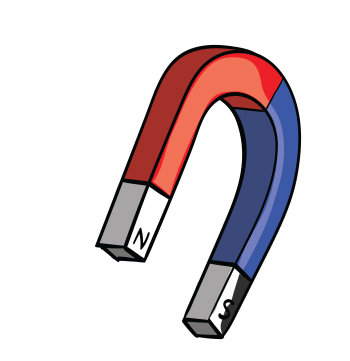
How do magnets work?
During this unit of work, children will explore simple pushes and pulls as an introduction to forces. They will explore how the texture of an object or the surface it is on can affect how the object moves. They will then explore pushes and pulls further by investigating different magnets and how they can pull (attract) and push (repel) at a distance without contact.
Light
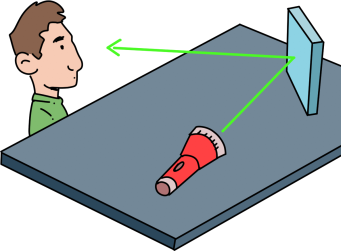
How does light travel?
During this unit of work, children will recognise that they need light in order to see things and that dark is the absence of light. They will learn to identify light sources; explore what happens when light reflects off mirrors or other reflective materials and think of ways to protect themselves from the Sun. They will investigate which materials make the best/worst shadows and conduct an experiment to find out about the relationship between the height of a light source and the length of a shadow. Children will also experience a range of activities to discover how mirrors work.
Plants

How does each part of a plant fulfil its function?
During this unit of work, children will build upon their previous knowledge of plants and trees from Year 2 where children find out what plants need in order to stay healthy once they have grown. Throughout this topic, children will be creating a booklet of what they find out which they can then give to Y6 pupils to help with their SATs revision. This gives them a real life context for their work. They will identify and describe the functions of the different parts of plants. They will explore what plants need for life and growth. Children will then complete an investigation to see how water is transported through plants. Children will also look at seeds and explore the different ways that plants disperse their seeds.
Y4
Animals, including
humans

How is energy transferred in living things?
During this unit of work, children will learn about the importance of the digestive system. They will learn the names and functions of each part of the system and be able to identify the different types of teeth in humans and their purpose. The children will plan and conduct an investigation to answer the question: which drink causes the most tooth decay? They will extend their knowledge of food chains by constructing and interpreting a variety of food chains, identifying producers, predators and prey.
States of matter

How does temperature affect different materials?
During this unit of work, children will learn to compare and group materials according to whether they are solids, liquids or gases. They will learn that some materials change state when they are heated or cooled and be able to identify and name these processes as melting, freezing, evaporating or condensing. They will learn about the water cycle and be able to identify the part played by evaporation and condensation in the water cycle. Children will work scientifically to plan and conduct investigations involving melting and evaporation. They will learn to associate the rate of evaporation with temperature.
Sound

How does sound travel?
During this unit of work, children will learn how vibrations cause sounds and how sounds travel through different mediums at different speeds. They will explore how sounds can change in pitch and loudness and be able to explain this using scientific language. They will develop their scientific skills by planning two fair test investigations to answer the questions: which material is the best at muffling sounds and does the size of the pinnae affect the volume of the sound? Children will also learn what happens to sound vibrations when they reach the ear.
Electricity

How does electricity travel?
During this unit of work, children will learn to sort common electrical appliances into battery and mains powered. They will construct simple series circuits containing a variety of components and understand the difference between complete and incomplete circuits. They will be able to identify whether or not a bulb will light in a simple series circuit and put forward ideas to fix incomplete circuits. The children will plan and conduct an investigation to discover which materials make good insulators and design, construct and test their own switches.
Living things and
their habitats

How can the environment affect different groups of animals?
During this unit of work, children will learn to recognise the seven life processes common to all living things. They will learn to sort living things using a variety of criteria and extend their use of scientific vocabulary to describe features and characteristics of animals and plants. They will conduct a local habitat search and learn to identify unknown living things using a classification key. Children will consider how environmental change impacts the local area and suggest ways in which humans can prevent further damage.
Y5
Animals, including
humans

How do we change as we grow older?
During this unit of work, children will learn about the different stages of the human life cycle. They will discuss a simple timeline first before going into more depth about what happens in the womb, during puberty and when you are older.
Properties and changes
of materials
How do we separate materials?
During this unit of work, children will consolidate previous learning by revisiting the properties of solids, liquids and gases; learn to describe the properties of materials using scientific language; investigate which materials make the best thermal insulators; and which materials are magnetic. Children will be introduced to key scientific vocabulary to describe the properties of materials (e.g. soluble and insoluble) and investigate how to separate materials using these properties. They will be able to name separation methods (filtering, sieving, evaporation, magnets) and decide on the most efficient method for separating a mixture of materials.
Earth and space
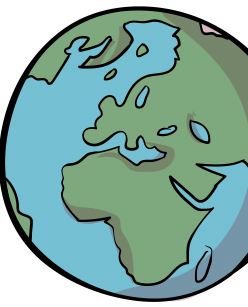
How does the Earth fit into our solar system?
During this unit of work, children will learn that the Earth is part of the solar system and that the Sun is at the centre of that system. They will learn the names of the other planets (based on their distance from the Sun) and be able to describe the movement of Earth (and other planets) in relation to the Sun. Children will discover why there is day and night on Earth and relate this to time. They will plan an investigation to answer the question - what happens to the Sun during the daytime? Children will also gain an understanding of the phases of the Moon and be able to describe the Moon’s movement in relation to the Earth.
Forces
How can we observe forces?
During this unit of work, children will consolidate and extend their knowledge of forces by naming individual forces (e.g. gravity, friction, upthrust). They will extend their knowledge of frictional forces (air resistance and water resistance) and plan fair test investigations to discover which shoe has the greatest friction and which shapes offer the most water resistance. They will learn how forces can be helpful and unhelpful in various scenarios and identify the forces involved in each scenario. They will learn what a mechanism is and how pulleys, levers and gears are used to allow a smaller force to have a greater effect.
Living things and
their habitats

How do different living things reproduce?
During this unit of work, children will learn the seven life processes that distinguish living from non-living things. They will consolidate and extend previous learning on the life cycles of plants and animals, comparing and describing differences in the life cycles of mammals, amphibians, reptiles, birds and insects. They will learn how animals and plants reproduce; comparing differences and similarities between five different animal groups.
Y6
Animals, including
humans

How do an animal's living systems work together to maintain a healthy body?
During this unit of work, children will learn about the importance of the circulatory system and how it transports oxygen around our body. They will learn about the heart and how it is an important muscle in our bodies. Children will learn about their heart rate and different activities that can increase the heart rate. Children will learn about being healthy and things they can do to lead a healthy lifestyle as well as learning about things that people do that can cause them to be unhealthy.
Electricity
How can circuits vary?
During this unit of work, children will consolidate and extend previous learning from year 4 by constructing simple series circuits and drawing them using scientific symbols. They will conduct investigations to determine how the voltage in a circuit affects the brightness of a bulb. They will use their ‘working scientifically’ skills to plan an experiment to investigate variations in how components function and use the results to write a clear and concise conclusion. They will use the internet to research information about renewable and non-renewable energy sources and communicate this information in the form of a leaflet.
Evolution and inheritance
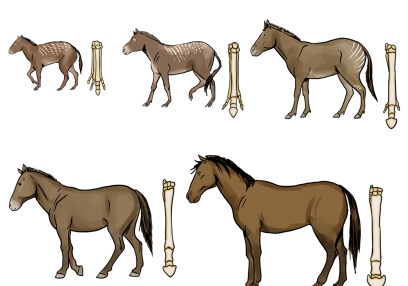
How have living things evolved over time?
During this unit of work, children will explore how animals and plants are adapted to the environment in which they live. They will learn that adaptations occur over time and that may lead to a species evolving. Children will conduct an experiment to answer the question - which beak is best adapted to pick up a seed? They will consider how certain adaptations occur in response to environmental conditions. They will learn about natural selection and how this links to inheritance and how some characteristics are inherited from parents and some are not. Children will consolidate previous learning on fossilisation and understand how studying fossils has helped explain the theory of evolution.
Living things and
their habitats

How can we classify living things into specific groups?
During this unit of work, children will learn about classification of living things, including microorganisms. They will learn the names and characteristics of the main groups used to classify animals, plants and microorganisms. Children will learn to use a classification key and create their own key using yes/no questions. Children will investigate the question; Is yeast a microorganism? And conduct an experiment involving the respiration of yeast. They will produce a presentation about the life and work of Carolus Linnaeus and understand the importance of his standard classification system.
Light

How do our eyes work?
During this unit of work, children will consolidate previous learning by exploring the way that light behaves, including light sources, reflection and shadows. Pupils will make predictions and investigate the relationship between light sources, objects and shadows and understand how the eye works. Children will extend their experience of light by looking at rainbows, prisms and bending light in water (although they don’t need to explain why these phenomena occur at this stage).
